RNase R
|
Cat. No.
|
E049
Print
|
|
Name
|
RNase R
|
|
Unit
|
500 U (50 μl)
|
|
Category
|
Molecular Biology Enzymes and Kits
|
|
Description
|
 |
Save when you buy abm's RNase R bundled with RNaseOFF Ribonuclease Inhibitor. Click here and add this bundle to your cart to save instantly!
|
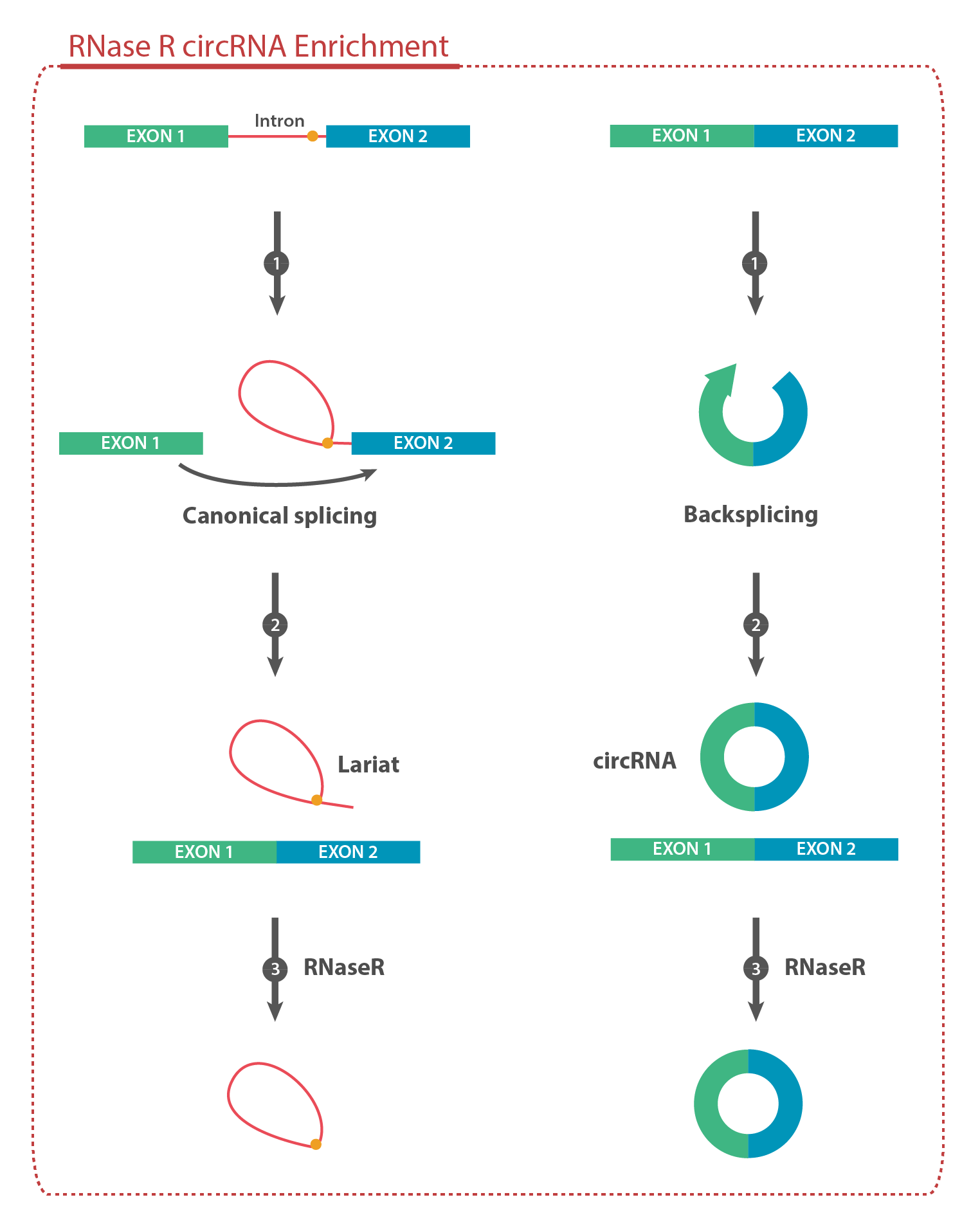
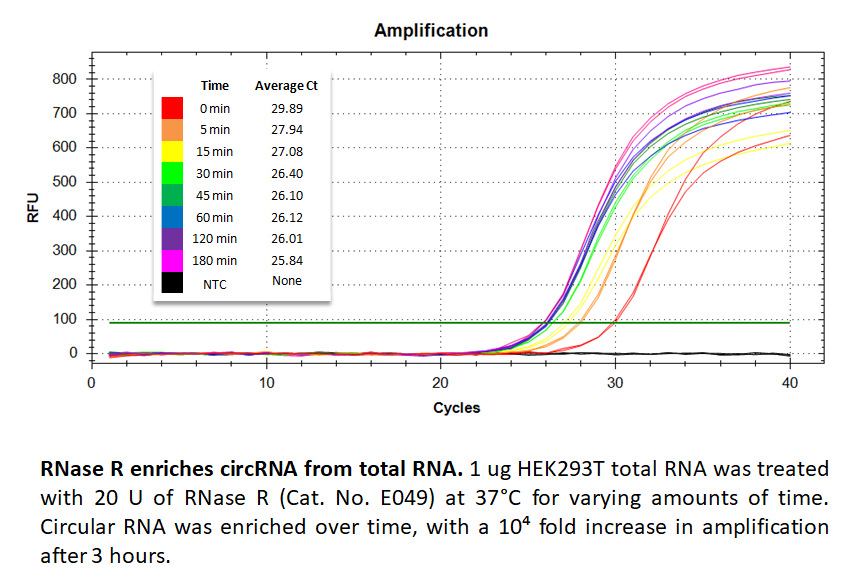
RNase R is an E. coli exoribonuclease that exhibits 3'-to-5' exonuclease activity, efficiently digesting nearly all linear RNA species. This enzyme does not digest circular, lariat, or double-stranded RNA with short 3’ overhangs (less than seven nucleotides). As such, this enzyme is ideally suited to the study of lariat RNA produced by traditional splicing, as well as circRNAs which arise through back-splicing. By removing linear RNAs from cellular or RNA extracts, RNase R greatly facilitates the identification of circular species through RNA-sequencing. This enables researchers to probe the landscape of splicing events with greater depth.
| Product Component |
Quantity |
| RNase R (10 U/µl) |
50 µl |
| 10X RNase R Reaction Buffer |
1.0 ml |
|
|
Application
|
- Enriching circRNAs in biological samples
- Identification of intronic lariat sequences
- Identification of exonic circRNAs
- Studying alternative splicing
- Production of artificial circular RNAs
|
|
Concentration
|
10 U/μl
|
|
Format General
|
Enzyme supplied with 10X Reaction Buffer.
|
|
Expression System General
|
Recombinant E. coli
|
|
Reaction Definition
|
Use 1X RNase R Reaction Buffer and incubate at 37°C. One unit is defined as the amount of RNase R that converts 1 µg of poly(A) into acid-soluble nucleotides in 10 minutes at 37°C.
|
|
Reaction Buffer
|
200 mM Tris-HCl, 1 M KCl, 10 mM MgCl2, pH 7.5
|
|
Storage Buffer
|
50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 100mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, and 50% (v/v) Glycerol.
|
|
Storage Condition
|
Store all components at -20 °C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles of all components to retain maximum performance. All components are stable for 1 year from the date of shipping when stored and handled properly.
|
|
Note
|
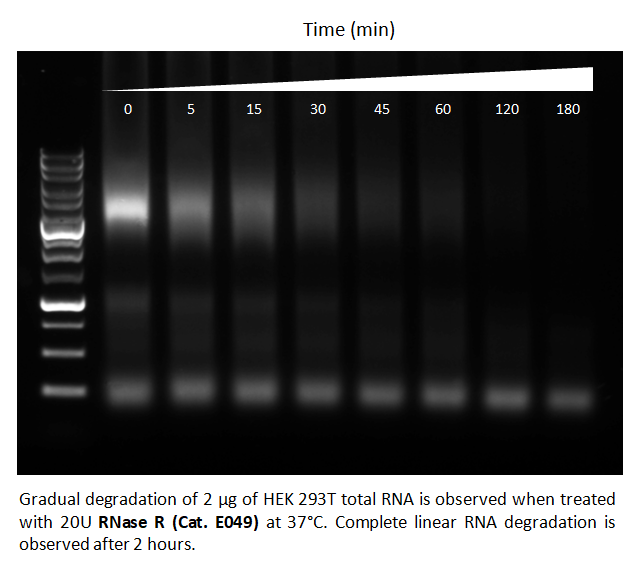
1) If degradation is inefficient, use a slightly higher incubation temperature (40-45°C) and supplement additional enzyme partway (e.g. 0.5 µl after 1 hour) through the procedure. The higher temperature is particularly useful for degrading highly structured linear RNAs, such as rRNAs. Do not exceed 45°C or incubate over 3 hours, as this may lead to non-enzymatic RNA degradation.
2) Magnesium at concentrations of 0.1-1.0 mM is required for optimal activity. If EDTA is present, compensate by adding MgCl2 to 1.0 mM final.
3) RNase R exhibits low activity on tRNA, rRNA and other highly structured RNAs, for which the 3’ end is double stranded with a short 3’ overhang. These RNA species can stall the enzyme and result in greatly reduced activity. For best results, removal of rRNA from total RNA extracts is highly recommended.
|
|
Caution
|
This product is distributed for laboratory research only. Not for diagnostic use.
|
|
Material Citation
|
If use of this material results in a scientific publication, please cite the material in the following manner: Applied Biological Materials Inc, Cat. No. E049
|
|
|
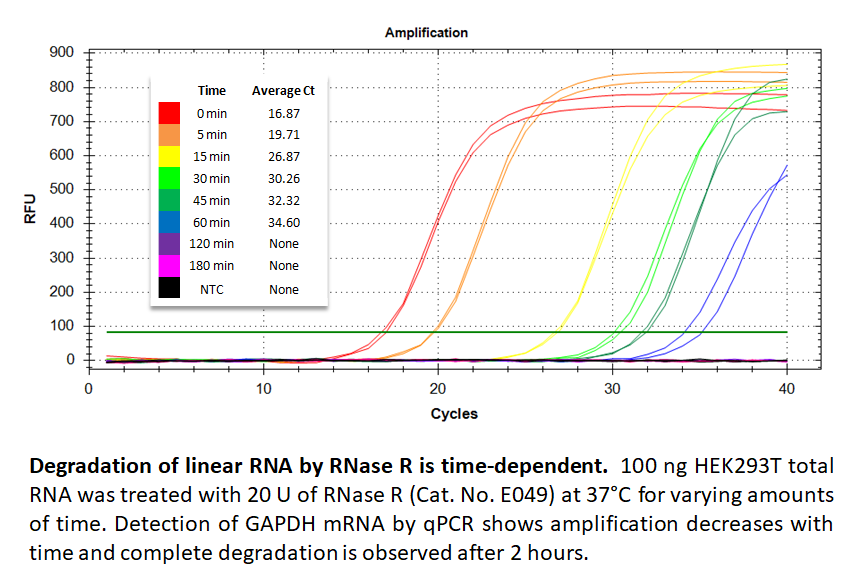
How efficiently will RNase R (when best optimized) digest linear RNA?
|
|
To calculate the percentage of digested linear RNA in your experiment, perform the following steps:
Step 1. Determine the Ct difference (ΔCt) between the Treated (+RNase R) and Untreated (No RNase R) Set.
Step 2. Calculate the fold change using the ΔCt value: Fold Change = 2ΔCt
Step 3. Calculate the percentage of RNA degraded using the fold change: % RNA Degraded = (1 - (1 / Fold Change)) × 100
For example, if your Treated Set has Ct=28.55 and Untreated Set has Ct = 18.01, the calculation will be:
ΔCt = 28.55 – 18.01 = 10.54
Fold Change = 2ΔCt = 210.54 = 1488.87
% RNA Degraded = (1-(1/1488.87)) × 100 = 99.93%
|
|
|
What inhibits RNase R?
|
|
Activity of the enzyme will be abolished if EDTA is present at a concentration of 1 mM or higher. Therefore, if using EDTA compensate by adding MgCl₂ to 1.0 mM final concentration.
|
|
|
How is RNase R inactivated/removed?
|
|
While the enzyme can be heat inactivated, the procedure is not recommended since high heat can lead to RNA damage. Phenol-chloroform precipitation can be used instead. For NGS, solid phase reversible immobilization (SPRI) bead cleanup is recommended.
|
|
|
Can I use higher temperatures (50°C) for my sample incubation?
|
|
While some of the literature reports that RNase R enzyme is active at temperatures equal or slightly higher than 50°C, we do not recommend exceeding the suggested range of 37-45°C. For NGS applications, incubation at 37°C is recommended. This will ensure optimal activity of the enzyme and absence of non-enzymatic degradation.
|
-
Wesselhoeft, R. A., Kowalski, P. S., Parker-Hale, F. C., Huang, Y., Bisaria, N., & Anderson, D. G. "RNA Circularization Diminishes Immunogenicity and Can Extend Translation Duration In Vivo" Molecular cell 74(3):508-520 (2019).
Vay, K. L., Salibi, E., Ghosh, B., Dora Tang, T.-Y., & Mutschler, H. (2022). Ribozyme-phenotype coupling in peptide-based coacervate protocells. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.10.25.513667
Peng, L., Chen, J., Li, M., & Wang, R. (2022). Circ_MBNL3 Restrains Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Sponging miR-873-5p to Release PHF2. Biochemical Genetics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10295-4
Zhang, S., Shen, Z., Chao, G., Du, X., Zhang, W., Jin, D., & Liu, Y. (2022). Circ_0004712 Silencing Suppresses the Aggressive Changes of Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes by Targeting miR-633/TRAF6 Axis. Biochemical Genetics, 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10265-w
Fu, C., Wang, J., Hu, M., & Zhou, W. (2022). Circ_0005615 contributes to the progression and Bortezomib resistance of multiple myeloma by sponging miR-185-5p and upregulating IRF4. Anti-Cancer Drugs, 33(9), 893-902. https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0000000000001378
He, M., Jia, Z., Wen, Y., & Chen, X. (2022). Circ_0043947 contributes to interleukin 1β-induced injury in chondrocytes by sponging miR-671-5p to up-regulate RTN3 expression in osteoarthritis pathology. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 17(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-022-02970-4
Li, J., Liu, X., Dong, S., Liao, H., Huang, W., & Yuan, X. (2022). Circ_0101802 Facilitates Colorectal Cancer Progression Depending on the Regulation of miR-665/DVL3 Signaling. Biochemical Genetics, 60(6), 2250–2267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10207-6
Xie, H., Yao, J., Wang, Y., & Ni, B. (2022). Exosome-transmitted circVMP1 facilitates the progression and cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting miR-524-5p-METTL3/SOX2 axis. Drug Delivery, 29(1), 1257–1271. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2022.2057617
Gao, X., Xu, N., Miao, K., Huang, G., & Huang, Y. (2022). Circ_0136666 aggravates osteosarcoma development through mediating miR-1244/CEP55 axis. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 17(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-022-03303-1
Li, Z., Wang, Z., Yang, S., Shen, C., Zhang, Y., Jiang, R., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Y., & Hu, H. (2022). CircSTK39 suppresses the proliferation and invasion in Bladder Cancer via regulating miR-135a-5p/NR3C2-mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition signaling pathway. Cell Biology & Toxicology. To https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1867978/v1
Zhang, M., Mou, L., Liu, S., Sun, F., & Gong, M. (2021). Circ_0001103 alleviates IL-1β-induced chondrocyte cell injuries by upregulating SIRT1 via targeting miR-375. Clinical Immunology, 227, 108718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2021.108718
Liu, Y., Wang, S., Pan, S., Yan, Q., Li, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2022). Circ_0000463 contributes to the progression and glutamine metabolism of non‐small‐cell lung cancer by targeting miR‐924/SLC1A5 signaling. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis, 36(1), e24116. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.24116
Ma, L., Liu, W., & Li, M. (2022). Circ_0061140 Contributes to Ovarian Cancer Progression by Targeting miR-761/LETM1 Signaling. Biochemical Genetics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10277-6
Omata, Y., Okawa, M., Haraguchi, M., Tsuruta, A., Matsunaga, N., Koyanagi, S., & Ohdo, S. (2022). RNA editing enzyme ADAR1 controls miR-381-3p-mediated expression of multidrug resistance protein MRP4 via regulation of circRNA in human renal cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 298(8), 102184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102184
Ou, H., Li, J., Lv, Q., & Feng, D. (2022). Hsa_circ_0069094 positively regulates the expression of oncogenic ZNF217 by competitively targeting miR-758–3p to promote the development of breast cancer. Reproductive Biology, 22(4), 100708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.repbio.2022.100708
Wang, F., Zhong, S., Mao, C., Jin, J., & Wang, H. (2022). Circ_0000291 contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis by binding to miR-1322 to up-regulate UBE2T. Annals of Hepatology, 100722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aohep.2022.100722
Zhang, H., Huang, T., Yuan, S., Long, Y., Tan, S., Niu, G., ... & Yang, M. (2022). Circ_0020123 plays an oncogenic role in non‐small cell lung cancer depending on the regulation of miR‐512‐3p/CORO1C. Thoracic Cancer, 13(9), 1406-1418. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.14408
Zhao, Y., Wang, S., Liu, S., Yan, Q., Li, Y., & Liu, Y. (2022). CircHSPG2 absence weakens hypoxia-induced dysfunction in cardiomyocytes by targeting the miR-25-3p/PAWR axis. Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy, 12(5), 589-602. https://doi.org/10.21037/cdt-22-197
Zhu, C., Jiang, X., Xiao, H., & Guan, J. (2022). Circ_0030998 Restrains Cisplatin Resistance Through Mediating miR-1323/PDCD4 Axis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Biochemical Genetics, 1-21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-022-10220-9
-
Alfonso-Gonzalez, C., Holec, S., Gorey, S., Shi, M., Rauer, M., Carrasco, J., ... & Hilgers, V. (2024). ELAV mediates circular RNA biogenesis in neurons. bioRxiv, 2024-06. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.22.600180
De Tomi E, Orlandi E, Belpinati F, Patuzzo C, Trabetti E, Gomez-Lira M, Malerba G. New Axes of Interaction in Circ_0079593/miR-516b-5p Network in Melanoma Metastasis Cell Lines. Genes (Basel). 2024 Dec 21;15(12):1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121647. PMID: 39766913; PMCID: PMC11675925.
Drula, R., Braicu, C., Chira, S., & Berindan-Neagoe, I. (2023). Investigating circular RNAs using qRT-PCR; roundup of optimization and processing steps. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5721. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065721
Frei, J., Jarzebska, N.T., Mellett, M., Kündig, T.M., Pascolo, S., Reichmuth, A.M. (2024). Design and Synthesis of Circular RNA Expression Vectors. In: Kramps, T. (eds) RNA Vaccines. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2786. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3770-8_9
Hu, Q., Zhao, H., Zhou, K., Hua, X., & Zhang, X. (2024). Scarless circular mRNA-based CAR-T cell therapy elicits superior anti-tumor efficacy. bioRxiv, 2024-08. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.08.05.606578
Liu, W., Yin, C., & Liu, Y. (2021). Circular RNA circ_0091579 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through miR-490-5p/CASC3 axis. Cancer Biotherapy & Radiopharmaceuticals, 36(10), 863-878. https://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2019.3472
Massu A, Mahanil K, Limkul S, Phiwthong T, Boonanuntanasarn S, Teaumroong N, Somboonwiwat K, Boonchuen P. Identification of immune-responsive circular RNAs in shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) upon yellow head virus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024 Jan;144:109246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2023.109246. Epub 2023 Nov 25. PMID: 38013134.
Nanishi, K., Konishi, H., Shoda, K., Arita, T., Kosuga, T., Komatsu, S., ... & Otsuji, E. (2020). Circulating circERBB2 as a potential prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer: an investigative study. Cancer Science, 111(11), 4177-4186. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14645
Ron, M., Ulitsky, I. Context-specific effects of sequence elements on subcellular localization of linear and circular RNAs. Nat Commun 13, 2481 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30183-0
Takaki, W., Konishi, H., Shoda, K. et al. Significance of Circular FAT1 as a Prognostic Factor and Tumor Suppressor for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 28, 8508–8518 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-021-10089-9
Ungerleider, N., Concha, M., Lin, Z., Roberts, C., Wang, X., Cao, S., ... & Flemington, E. K. (2018). The epstein barr virus circRNAome. PLoS pathogens, 14(8), e1007206. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1007206
Wesselhoeft, R. A., Kowalski, P. S., Parker-Hale, F. C., Huang, Y., Bisaria, N., & Anderson, D. G. (2019). RNA circularization diminishes immunogenicity and can extend translation duration in vivo. Molecular cell, 74(3), 508-520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.02.015
This product has no review yet.
Controls and Related Product:
UNIT
500 rxn (4 x 1.25 ml)
{"id":3210,"cat_no":"E049","sku_in_m2":"","old_cat_no":"E049","name":"RNase R","category_id":186,"category_name":"Molecular Biology Enzymes and Kits","frontend_category_id":6,"frontend_category_ids":"1,6","gene_id":0,"gene_name":"","gene_full_name":"","alias":"","unit_quantity":"500 U (50 \u03bcl)","accession_number":"","species_id":0,"species":"","raised_in_id":0,"raised_in":"","cell_type_id":0,"cell_type":"","tissue_id":0,"tissue":"","price":"319.0000","price_before_discount":"0.0000","keywords":"","invisible_search_keywords":"rnaser, rnase,Molecular Biology Enzymes and Proteins, circrna, lariat, circular rna, circrna enrichment. circular rna enrichment","filter_group_id":34,"filter_group_name":"Molecular Biology","filter_id":41,"filter_name":"Kits \u0026 Other Enzymes","search_filter_ids":"32,34","search_filter_keys":"32-34","temp_field":null,"customization":0,"filter_table_id":18084840,"filter_table_name":"","related_group_id":17,"url":"","operator":"","points_rule":7,"status":1,"need_remove":0,"document_sort":"","price_old":"295.0000","price2024":"310.0000","created_at":null,"updated_at":"2025-03-26 17:25:48","Confirmed":"Tony Confirmed","geo_price_before_discount":"0.00","geo_titer7_price_before_discount":"149.00","cate_url":"Molecular-Biology-Enzymes-and-Kits.html","frontendBreadcrumbs":[{"id":1,"pid":86,"name":"General Materials","page_id":27,"page_type":"App\\Models\\Category","href":null,"sort":1,"show_in_nav":1,"show_in_homepage":1,"has_children":1,"status":1,"related_table":null,"created_at":null,"updated_at":null,"url_key":"general-materials.html","url":"general-materials.html"},{"id":6,"pid":1,"name":"Enzymes \u0026 Kits","page_id":186,"page_type":"App\\Models\\Category","href":null,"sort":6,"show_in_nav":1,"show_in_homepage":1,"has_children":1,"status":1,"related_table":null,"created_at":null,"updated_at":null,"url_key":"Molecular-Biology-Enzymes-and-Kits.html","url":"Molecular-Biology-Enzymes-and-Kits.html"}],"price_flag":0,"builderURL":"","builderViewerURL":"","mapURL":"","viewerURL":"","builderType":"","productType":"App\\Models\\CatalogBaseMolecular","geo_price":"319.00","geo_price_symbol":"$319.00","category":{"id":186,"categories":"Molecular Biology Enzymes and Kits","pid":27,"url_key":"Molecular-Biology-Enzymes-and-Kits.html","css":"\/assets\/css\/abm.search.css,\/assets\/css\/abm.other.css,\/assets\/css\/abm.categorys.css, \/assets\/css\/ryan.temp.css","wid":0,"breadcrumbs":"[{\u0022url\u0022:\u0022https:\/\/www.abmgood.com\u0022,\u0022title\u0022:\u0022Home\u0022},{\u0022url\u0022:\u0022https:\/\/www.abmgood.com\/general-materials.html\u0022,\u0022title\u0022:\u0022General Materials \u0026amp; Others\u0022},{\u0022url\u0022:\u0022https:\/\/www.abmgood.com\/Molecular-Biology-Enzymes-and-Kits.html\u0022,\u0022title\u0022:\u0022Molecular Biology Enzymes and Kits\u0022}]","breadcrumbsIdJson":"\u003Cscript type=\u0022application\/ld+json\u0022\u003E{\u0022@context\u0022:\u0022https:\/\/schema.org\u0022,\u0022@type\u0022:\u0022BreadcrumbList\u0022,\u0022itemListElement\u0022:[{\u0022@type\u0022:\u0022ListItem\u0022,\u0022position\u0022:1,\u0022name\u0022:\u0022Home\u0022,\u0022item\u0022:\u0022https:\/\/www.abmgood.com\u0022},{\u0022@type\u0022:\u0022ListItem\u0022,\u0022position\u0022:2,\u0022name\u0022:\u0022General Materials \u0026amp; Others\u0022,\u0022item\u0022:\u0022https:\/\/www.abmgood.com\/general-materials.html\u0022},{\u0022@type\u0022:\u0022ListItem\u0022,\u0022position\u0022:3,\u0022name\u0022:\u0022Molecular Biology Enzymes and Kits\u0022}]}\u003C\/script\u003E","breadcrumbsHtml":"\u003Cul class=\u0022abm-breadcrumb\u0022\u003E\u003Cli\u003E\u003Ca href=\u0022https:\/\/www.abmgood.com\u0022\u003EHome\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/li\u003E\u003Cli\u003E\u003Ca href=\u0022https:\/\/www.abmgood.com\/general-materials.html\u0022\u003EGeneral Materials \u0026amp; Others\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/li\u003E\u003Cli class=\u0022active\u0022\u003EMolecular Biology Enzymes and Kits\u003C\/li\u003E\u003C\/ul\u003E","description":"\u003Ch2 class=\u0022abm-categories-title-h2\u0022\u003EMolecular Biology Enzymes and Kits\u003C\/h2\u003E\n\u003Cul class=\u0022abm-page-category-nav-list\u0022 style=\u0022margin-top: -20px;\u0022\u003E\n\u003Cli class=\u0022abm-page-category-nav-item\u0022\u003E\u003Ca href=\u0022#Cloning-Applications\u0022 class=\u0022abm-page-category-nav-link abm-page-category-target-link\u0022\u003E Cloning Applications\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/li\u003E\n\u003Cli class=\u0022abm-page-category-nav-item\u0022\u003E\u003Ca href=\u0022#DNA-RNA-Applications\u0022 class=\u0022abm-page-category-nav-link abm-page-category-target-link\u0022\u003E DNA \u0026amp; RNA Applications\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/li\u003E\n\u003Cli class=\u0022abm-page-category-nav-item\u0022\u003E\u003Ca href=\u0022#in-vitro-Kits-Proteases\u0022 class=\u0022abm-page-category-nav-link abm-page-category-target-link\u0022\u003EProteases\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/li\u003E\n\u003Cli class=\u0022abm-page-category-nav-item\u0022\u003E\u003Ca href=\u0022\/rnase-r-e049.html\u0022 class=\u0022abm-page-category-nav-link abm-page-category-target-link\u0022\u003E RNase R\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/li\u003E\n\u003Cli class=\u0022abm-page-category-nav-item\u0022\u003E\u003Ca href=\u0022\/cas9-proteins.html\u0022 class=\u0022abm-page-category-nav-link abm-page-category-target-link\u0022\u003ECas Proteins \u0026amp; CRISPR Screening\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/li\u003E\n\u003C\/ul\u003E\n\u003Cdiv class=\u0022abm-container-fluid\u0022\u003E\n\u003Cdiv class=\u0022row\u0022\u003E\n\u003Cdiv class=\u0022col-md-12\u0022 style=\u0022text-align: left; padding-bottom: 3em;\u0022\u003E\n\u003Cp\u003E\u003Cstrong\u003Eabm\u003C\/strong\u003E offers a variety of high quality individual enzymes and kits that enable the preparation of DNA and RNA for subsequent downstream applications such as assay development, PCR, restriction digest, cloning and sequencing. Simplify your experiments with our trusted products for consistent, high-performance results.\u003C\/p\u003E\n\u003Cdiv class=\u0022table-responsive\u0022\u003E\n\u003Ctable class=\u0022bootstrap-table bootstrap-table-hover abm-service-table abm-perfect-table1\u0022 style=\u0022--first-child-white-space: nowrap;\u0022\u003E\n\u003Cthead\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Cth\u003EProduct Name\u003C\/th\u003E\n\u003Cth\u003ECat. No.\u003C\/th\u003E\n\u003Cth\u003ESize\u003C\/th\u003E\n\u003Cth\u003EPrice\u003C\/th\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003C\/thead\u003E\n\u003Ctbody\u003E\n\u003Ctr style=\u0022background-color: #f8f9fa;\u0022 align=\u0022left\u0022 class=\u0022abm-page-menu only-hide\u0022 id=\u0022Cloning-Applications\u0022\u003E\n\u003Ctd colspan=\u00224\u0022 style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Cspan style=\u0022color: #000;\u0022\u003E\u003Cstrong\u003ECloning Applications\u003C\/strong\u003E\u003C\/span\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/pro-ligation-free-cloning-kit-e086.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EPro Ligation-Free Cloning Kit (20 reactions)\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/pro-ligation-free-cloning-kit-e086.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EE086\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E20 Reactions\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022E086\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$150.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/pro-ligation-free-cloning-kit-e087.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EPro Ligation-Free Cloning Kit (50 reactions)\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/pro-ligation-free-cloning-kit-e087.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EE087\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E50 Reactions\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022E087\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$250.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/proclone-competent-cells-3.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EProClone\u0026trade; Competent Cells\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/proclone-competent-cells-3.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EE003\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E1.2 ml (6 x 200 \u0026micro;l)\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022E003\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$150.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/phi29-dna-polymerase-e014.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EUltra-Pure Phi29 DNA Polymerase\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/phi29-dna-polymerase-e014.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EE014\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E100 \u0026micro;l\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022E014\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$152.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr style=\u0022background-color: #f8f9fa;\u0022 align=\u0022left\u0022 class=\u0022abm-page-menu only-hide\u0022 id=\u0022DNA-RNA-Applications\u0022\u003E\n\u003Ctd colspan=\u00224\u0022 style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Cspan style=\u0022color: #000;\u0022\u003E\u003Cstrong\u003EDNA \u0026amp; RNA Applications\u003C\/strong\u003E\u003C\/span\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/rnase-r-e049.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003ERNase R\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/rnase-r-e049.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EE049\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E500 U (50 \u0026mu;l)\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022E049\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$310.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/rnaseoff-ribonuclease-inhibitor.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003ERNaseOFF Ribonuclease Inhibitor\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/rnaseoff-ribonuclease-inhibitor.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EG138\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E4,000 U (100 \u0026micro;l)\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022G138\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$80.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/rnaseoff-ribonuclease-inhibitor-g591.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003ERNaseOFF Ribonuclease Inhibitor\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/rnaseoff-ribonuclease-inhibitor-g591.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EG591\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E100,000 U (2 x 1.25 ml)\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022G591\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$1400.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/rnaser-rnaseoff-bundle.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003ERNase R with RNaseOFF Bundle\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/rnaser-rnaseoff-bundle.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EE049-G138S\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003EBundle\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022E049-G138S\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$349.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/rnase-a-250.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003ERNase A\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/rnase-a-250.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EG117\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E25 mg\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022G117\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$57.50\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/dnase-i-g028.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EDNase I\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/dnase-i-g028.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EG028\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E2000 U (1.0 ml)\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022G028\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$89.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/dnase-i-rnase-free-e091.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EDNase I (RNase-Free)\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/dnase-i-rnase-free-e091.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EE091\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E200 U (100 \u0026mu;l)\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022E091\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$99.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/poly-a-polymerase-yeast-e017.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EPoly(A) Polymerase, Yeast\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/poly-a-polymerase-yeast-e017.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EE017\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E100 U (100 \u0026mu;l)\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022E017\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$52.50\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/polyA-polymerase-e.coli-e099.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EPoly(A) Polymerase, \u003Cem\u003EE. coli\u003C\/em\u003E\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/polyA-polymerase-e.coli-e099.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EE099\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E25 U (25 \u0026micro;l)\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022E099\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$125.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/t7-rna-polymerase-e041.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003ET7 RNA Polymerase\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/t7-rna-polymerase-e041.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EE041\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E100 ul (5000 U)\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022E041\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$68.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/t4-gene-32-protein-e040-vin.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003ET4 Gene 32 Protein\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/t4-gene-32-protein-e040-vin.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EE040\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E100 \u0026mu;g\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022E040\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$52.50\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/thermolabile-udg.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EThermolabile UDG\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/thermolabile-udg.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EE095\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E200 reactions\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022E095\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$85.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/gfp-purified-protein-000033p.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EGFP Purified Protein\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/gfp-purified-protein-000033p.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003E000033P\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E50 \u0026mu;g\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022000033P\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$158.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr style=\u0022background-color: #f8f9fa;\u0022 align=\u0022left\u0022 class=\u0022abm-page-menu only-hide\u0022 id=\u0022in-vitro-Kits-Proteases\u0022\u003E\n\u003Ctd colspan=\u00224\u0022 style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Cspan style=\u0022color: #000;\u0022\u003E\u003Cstrong\u003EProteases\u003C\/strong\u003E\u003C\/span\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/e027name.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003ETEV Protease\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/e027name.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EE027\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E100 \u0026mu;l\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022E027\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$47.50\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/enterokinase-cleavage-enzyme-mammalian-produced-g699.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EEnterokinase Cleavage Enzyme (Mammalian Produced)\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/enterokinase-cleavage-enzyme-mammalian-produced-g699.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EG699\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left;\u0022\u003E100 Units\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022G699\u0022 data-type=\u0022molecular\u0022\u003E$115.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left; width: 30.8635%;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/proteinase-k-g029.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EProteinase K\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left; width: 14.6197%;\u0022\u003E\u003Ca class=\u0022orange-link\u0022 href=\u0022\/proteinase-k-g029.html\u0022 rel=\u0022noopener\u0022\u003EG029\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd style=\u0022text-align: left; width: 27.1058%;\u0022\u003E1.0 ml; 20mg\/ml\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd class=\u0022product-price\u0022 data-product=\u0022G029\u0022\u003E$92.00\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003C\/tbody\u003E\n\u003C\/table\u003E\n\u003C\/div\u003E\n\u003C\/div\u003E\n\u003C\/div\u003E\n\u003C\/div\u003E","meta_title":"Molecular Biology Enzymes and Kits","meta_keywords":"Molecular Biology Enzymes and Kits","meta_description":"Molecular Biology Enzymes and Kits","deleted_at":null,"enable":"Y","parent_list":"27","table_name":null,"image":null,"independentPage":0,"top_type":1,"sort_order":null,"in_footer":1,"fid":null,"created_at":null,"updated_at":"2025-04-02 01:04:45"},"info":{"id":18427,"cat_no_base":"E049","parent_id":3210,"description":"\u003Ctable style=\u0022border-collapse: collapse; background-color: #f9eae4; border-radius: 10px; vertical-align: middle; margin-bottom: 20px;\u0022 border=\u00220\u0022 cellpadding=\u002210\u0022\u003E\n\u003Ctbody\u003E\n\u003Ctr valign=\u0022middle\u0022\u003E\n\u003Ctd\u003E\u003Cimg src=\u0022\/assets\/images\/wysiwyg\/promotion-tag-v2.png\u0022 \/\u003E\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd\u003E\n\u003Cp\u003E\u003Cstrong\u003ESave\u003C\/strong\u003E when you buy \u003Cstrong\u003Eabm\u003C\/strong\u003E\u0027s \u003Cstrong\u003ERNase R\u003C\/strong\u003E bundled\u0026nbsp;with \u003Cstrong\u003ERNaseOFF Ribonuclease Inhibitor\u003C\/strong\u003E. Click \u003Cstrong\u003E\u003Ca href=\u0022\/rnaser-rnaseoff-bundle.html\u0022\u003Ehere\u003C\/a\u003E\u003C\/strong\u003E and add this bundle to your cart to save instantly!\u003C\/p\u003E\n\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003C\/tbody\u003E\n\u003C\/table\u003E\n\u003Cp\u003E\u003Cstrong\u003ERNase R\u003C\/strong\u003E is an\u003Cem\u003E \u003Cstrong\u003EE. coli\u003C\/strong\u003E \u003C\/em\u003Eexoribonuclease that exhibits \u003Cstrong\u003E3\u0027-to-5\u0027\u003C\/strong\u003E exonuclease activity, efficiently digesting nearly all linear RNA species. This enzyme does not digest \u003Cstrong\u003Ecircular\u003C\/strong\u003E, \u003Cstrong\u003Elariat\u003C\/strong\u003E, or \u003Cstrong\u003Edouble-stranded RNA\u003C\/strong\u003E with short 3\u0026rsquo; overhangs (less than seven nucleotides). As such, this enzyme is ideally suited to the study of \u003Cstrong\u003Elariat RNA\u003C\/strong\u003E produced by traditional splicing, as well as \u003Cstrong\u003EcircRNAs\u003C\/strong\u003E which arise through back-splicing. By removing linear RNAs from cellular or RNA extracts, \u003Cstrong\u003ERNase R\u003C\/strong\u003E greatly facilitates the identification of \u003Cstrong\u003Ecircular species\u003C\/strong\u003E through RNA-sequencing. This enables researchers to probe the landscape of \u003Cstrong\u003Esplicing events\u003C\/strong\u003E with greater depth.\u003C\/p\u003E\n\u003Ctable class=\u0022bootstrap-table bootstrap-table-hover abm-service-table abm-perfect-table2\u0022 style=\u0022margin: 20px 0;\u0022\u003E\n\u003Cthead\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Cth\u003E\u003Cstrong\u003EProduct Component\u003C\/strong\u003E\u003C\/th\u003E\n\u003Cth\u003E\u003Cstrong\u003EQuantity\u003C\/strong\u003E\u003C\/th\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003C\/thead\u003E\n\u003Ctfoot\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd\u003ERNase R (10 U\/\u0026micro;l)\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd\u003E50 \u0026micro;l\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003Ctr\u003E\n\u003Ctd\u003E10X RNase R Reaction Buffer\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003Ctd\u003E1.0 ml\u003C\/td\u003E\n\u003C\/tr\u003E\n\u003C\/tfoot\u003E\n\u003C\/table\u003E","disclaimer":null,"application":"\u003Cul\u003E\n\u003Cli\u003EEnriching circRNAs in biological samples\u003C\/li\u003E\n\u003Cli\u003EIdentification of intronic lariat sequences\u003C\/li\u003E\n\u003Cli\u003EIdentification of exonic circRNAs\u003C\/li\u003E\n\u003Cli\u003EStudying alternative splicing\u003C\/li\u003E\n\u003Cli\u003EProduction of artificial circular RNAs\u003C\/li\u003E\n\u003C\/ul\u003E","components":null,"cas9_origin":null,"concentration":"10 U\/\u03bcl","enzymes_size":null,"genecraft_series":null,"guarantee":null,"population":null,"qc":null,"format_general":"Enzyme supplied with 10X Reaction Buffer.","including_screening_kit":null,"expression_system_general":"Recombinant \u003Ci\u003EE. coli\u003C\/i\u003E","purity":null,"image":null,"insert_size":null,"shipping_conditions":null,"source_catalog_number":null,"inactivation_protocol":null,"led_viewer_compatibility":null,"unit_definition":null,"vector":null,"reaction_buffer":"200 mM Tris-HCl, 1 M KCl, 10 mM MgCl\u003Csub\u003E2\u003C\/sub\u003E, pH 7.5","storage_buffer":"50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 100mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, and 50% (v\/v) Glycerol.","caution":"This product is distributed for laboratory research only. Not for diagnostic use.","storage_condition":"Store all components at -20 \u00b0C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles of all components to retain maximum performance. All components are stable for 1 year from the date of shipping when stored and handled properly.","product_volume":null,"reporter":null,"safeview_series":null,"source_catno":null,"stain_color":null,"supplier":null,"internal_supplier":null,"internal_note":null,"inventory_location":null,"note":"\u003Cp\u003E1) If degradation is inefficient, use a slightly higher incubation temperature (40-45\u0026deg;C) and supplement additional enzyme partway (e.g. 0.5 \u0026micro;l after 1 hour) through the procedure. The higher temperature is particularly useful for degrading highly structured linear RNAs, such as rRNAs. Do not exceed 45\u0026deg;C or incubate over 3 hours, as this may lead to non-enzymatic RNA degradation.\u003C\/p\u003E\n\u003Cp\u003E2) Magnesium at concentrations of 0.1-1.0 mM is required for optimal activity. If EDTA is present, compensate by adding MgCl\u003Csub\u003E2\u003C\/sub\u003E to 1.0 mM final.\u003C\/p\u003E\n\u003Cp\u003E3) RNase R exhibits low activity on tRNA, rRNA and other highly structured RNAs, for which the 3\u0026rsquo; end is double stranded with a short 3\u0026rsquo; overhang. These RNA species can stall the enzyme and result in greatly reduced activity. For best results, removal of rRNA from total RNA extracts is highly recommended.\u003C\/p\u003E","recommend":null,"depositor":null,"licensor_name":null,"licensor_contact_information":null,"contract_termination_date":null,"royalty_rates":null,"cas_type":null,"cas_origin":null,"cas_protein_marker":null,"source":null,"endotoxin_level":null,"additional_information":null,"titer":null,"nucleotide_format":null,"protocol_overview":null,"source_price":null,"created_at":"2023-02-22 19:25:15","updated_at":"2025-03-25 18:47:42","short_description":null,"reaction_definition":"Use 1X RNase R Reaction Buffer and incubate at 37\u00b0C. One unit is defined as the amount of RNase R that converts 1 \u00b5g of poly(A) into acid-soluble nucleotides in 10 minutes at 37\u00b0C.","specificity":null,"promotions":null},"maps":[],"media":[{"id":379485,"parent_id":3210,"parent_type":"App\\Models\\CatalogBaseMolecular","file_path":"\/r\/n\/rnaser-circrna-enrichment_v4.png","title":null,"text":null,"file_type":"image","alt":null,"url":null,"position":1,"status":0,"entity_id_m2":18084840,"sku_in_m2":"E049","value_id_m2":49910086,"attribute_id":90,"created_at":"2022-07-19 04:36:22","updated_at":"2023-04-10 05:34:05"},{"id":383460,"parent_id":3210,"parent_type":"App\\Models\\CatalogBaseMolecular","file_path":"\/upload\/q6Av3WpIGC97Ssbio9C53ksYQ8m0zQHlPYXf3qov.png","title":null,"text":null,"file_type":"image","alt":null,"url":null,"position":2,"status":1,"entity_id_m2":null,"sku_in_m2":null,"value_id_m2":null,"attribute_id":0,"created_at":"2024-03-20 19:58:01","updated_at":"2024-03-20 19:58:05"},{"id":384868,"parent_id":3210,"parent_type":"App\\Models\\CatalogBaseMolecular","file_path":"\/upload\/nYAa5oGgyTf4xqSHq5PX0ERGg7sapcux7d949XP8.png","title":null,"text":null,"file_type":"image","alt":null,"url":null,"position":3,"status":1,"entity_id_m2":null,"sku_in_m2":null,"value_id_m2":null,"attribute_id":0,"created_at":"2024-03-26 20:49:49","updated_at":"2024-03-26 20:50:10"},{"id":384869,"parent_id":3210,"parent_type":"App\\Models\\CatalogBaseMolecular","file_path":"\/upload\/g9SwvPfeDyLMmhokHsQM0c0lsuwSionMZKLgfWjW.png","title":null,"text":null,"file_type":"image","alt":null,"url":null,"position":4,"status":1,"entity_id_m2":null,"sku_in_m2":null,"value_id_m2":null,"attribute_id":0,"created_at":"2024-03-26 20:49:54","updated_at":"2024-03-26 20:50:10"}],"gene":null}